Keratoconus
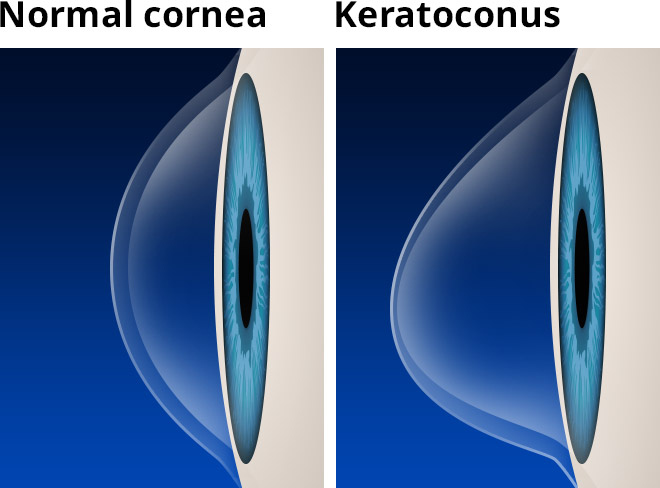
Keratoconus is a progressive eye condition whereby the round cornea thins and protrudes like a cone. This abnormality causes the light entering the eye to be deflected, resulting in distorted vision.
The onset usually occurs during teenage years to young adulthood and it can affect one or both eyes, of which the vision in both eyes can be very different.
What are the symptoms of Keratoconus?
- Distorted vision
- Progressive myopia
- Irregular astigmatism
- Increased sensitivity to light and glare
- Discomfort when wearing contact lenses because they do not fit properly
Recent studies have suggested that an imbalance of enzymes in the cornea exposes the eye to oxidative damage from free radicals which would lead to the weakening and bulging of the corneal tissue, resulting in keratoconus.
Other factors that could predispose one to keratoconus are overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays, excessive rubbing of the eyes, chronic eye irritation, and genetics.
What is the treatment for Keratoconus?
Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking (CXL)
This treatment comprises of using eyedrops containing riboflavin, a type of vitamin B, and a special UV light to activate and promote crosslinking of the corneal tissue to strengthen the cornea and halt the progression of the bulge or keratoconus. Corneal collagen cross-linking is also used as an additional treatment in refractive surgery.
Early diagnosis and treatment is crucial to prevent further weakening of the corneal tissues that could result in more serious complications.



